work product doctrine elements
Defining the Scope b. The work product doctrine is narrower than the attorney-client privilege because.
26b3A makes it clear that documents produced by non- attorneys may also enjoy work product privilege.

. Examples of work product. Legal advice of any kind is sought From a professional legal advisor in that capacity Communications made for that purpose In confidence By the client At the clients instance permanently protected Unless privilege is waived. The primary policy objective of the work-product doctrine is to preserve the effective assistance of attorneys and others employed to help prepare a case for trial.
In considering the companys arguments the Alabama Supreme Court repeated the elements of the work product doctrine. The work product doctrine protection rests on three elements. Who May Raise the Privilege.
However the work product doctrine is also narrower than the attorney-client privilege because its protections extend only to documents and other tangible things that are prepared in anticipation of litigation. The work product doctrine protects statements reports notes and other materials prepared by the criminal defense attorney in anticipation of or during litigation. The immunity is qualified in that it is subject to discovery by the opposing party upon a special showing of undue hardship or injustice.
In some ways the work product doctrine is broader than the attorney-client privilege because its protections are not limited solely to communications or confidential matters. Compilations of selected documents constitute work product. Documents or tangible things.
The work product doctrine is a qualified immunity from the discovery of an attorneys written statements private memoranda and personal recollections that are made in anticipation of litigation. Privileged Persons a Corporation as Client b Functional Equivalent Test. What constitutes work product.
The three basic work product elements are litigation discussed in Chapter 36 anticipation discussed in Chapter 37 and motivation discussed in Chapter 38. Courts Disagree About Basic Work Product Doctrine Elements. BASIC ELEMENTS Attorney-Client Privilege Attorney Work-Product Doctrine Introduction.
Litigation need only be imminent and includes actions such as grand jury proceedings investigations and administrative actions. Who can invoke the protections of the work product doctrine. Definition purpose of and history of work product doctrine.
Prepared in anticipation of litigation or for trial Applies in ADR and administrative actions 3. The Work Product Doctrine. The work product doctrine states that an adverse party generally may not discover or compel disclosure of written or oral materials prepared by or for an attorney in the course of legal representation especially in preparation for litigation.
Attorney-Client Privilege 200pm 220pm. It is also known as the work-product rule the work-product immunity the work-product exception and the work-product privilege though there is debate about whether it is truly a privilege This doctrine does not apply in other countries. This paper begins with a brief review of the basics of the attorney-client privilege and the work product doctrine.
The colorado supreme court codified the work product doctrine at crcp 26 b 3 effective april 1 1970. In American civil procedure the work-product doctrine protects materials prepared in anticipation of litigation from discovery by opposing counsel. The Federal Rules of Civil Procedure and most state court rules memorialize their basic work product doctrine in just one sentence.
2 The person to whom the communication was made is a member of the bar of a court or his subordinate. The work product doctrine is designed to encourage careful and thorough trial preparation by the lawyer. Below is a brief outline of the key elements of the attorney-client privilege and the attorney work- product doctrine both of which often provide essential protection for providers confidential communications during discovery.
Ordinarily a party may not discover documents and tangible things that areprepared in anticipation of litigation or for trial by or for another party or its representative including the other partys attorney consultant surety. Attorney-client privilege and the work product doctrine. Maintaining the privacy of communications between client attorney and others employed in preparing for litigation especially privacy in the development of legal theories opinions and strategies-the doctrine.
Materials prepared in anticipation of litigation or trial. A brief excerpt from Quimbees tutorial video on the purpose of the work product doctrine and its elements and also refer to Federal Rule of Civil Procedure. Some courts apply work product protection only to documents that litigants will use to assist in litigation.
Session I Attorney-Client Privilege Work Product Doctrine for In House Counsel 200pm 300pm 1. Elements of Work-Production Protection Work product protection has three required elements including. Most lawyers attention focuses on the second element whether their clients reasonably anticipate litigation.
And 2 it can be overcome -- if the adversary establishes substantial need for the withheld work product and the inability to obtain its substantial equivalent without undue hardship. Elements1 Three essential requirements for materials to be protected by the work product doctrine under Rule 26 b 3 of the Utah Rules of Civil Procedure. 1 The asserted holder of the privilege is or sought to become a client.
15 this rule allows discovery for information prepared in anticipation of litigation or for trial by or for another party or by or for that other partys representative 16 the rule qualifies this access by requiring a showing of. The material must consist of documents or tangible things 2. Documents and tangible things otherwise discoverable which are prepared in anticipation of litigation or trial by or for another party or by or for that other.
1 it applies only at certain times during or in anticipation of litigation. Prepared in Anticipation of Litigation. Who can produce work product.
In normal civil or criminal litigation the first element presents an easy analysis. 3 These four elements are. But courts take divergent views on what that sentence means.
Elements of the Work Product Doctrine. However under Rule 26 b 3 of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure an adverse party may discover or compel disclosure of work. Chapters 39 through 42 address work products content.
Elements of work product doctrine. 110 Protected Content. 06302010 1 Attorney-Client Privilege and Work Product Doctrine Attorney-Client Privilege Elements.
A Documents and Tangible Things. It then examines how those protections have been applied in the context of internal investigations focusing on ways in which one could preserve or lose the protections. During the course of representation.

Privilege And Work Product Considerations When Engaging Third Party Consultants The National Law Review

Privilege And Work Product In Insurance Coverage Disputes Barnes Thornburg

Theoretical Computer Science For The Working Category Theorist

4 4 Design Solution Definition Nasa

What Is A Privilege A Privilege Is A Relationship Between A Witness And The Subject Of Potential Testimony Whether That Subject Be A Person Or Something Ppt Download
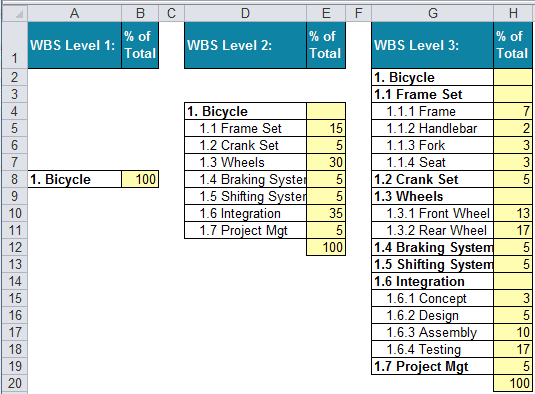
Work Breakdown Structure Wbs Elements Formats Best Practices Ecosys
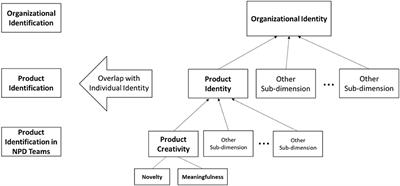
Frontiers Product Creativity As An Identity Issue Through The Eyes Of New Product Development Team Members Psychology

Ldquo In Anticipation Of Litigation Rdquo May Not Mean What You Think Jackson Kelly Pllc Blog Post